Wasp Stings In Children
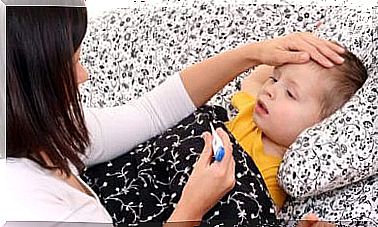
Wasp stings in children can produce intense pain. In these situations, mothers are worried and tend to resort to all kinds of measures. While the intention is always good, practice may not be the most advisable. Therefore, it is convenient to know how to proceed properly.
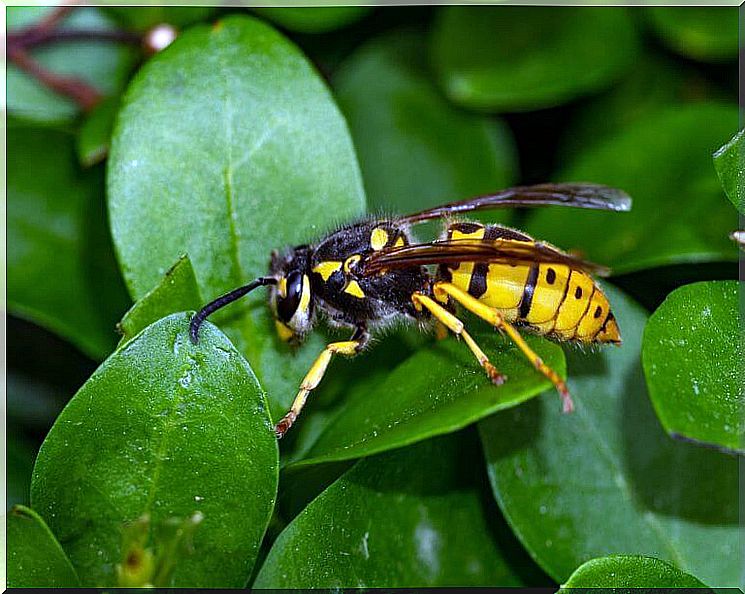
We must remember that wasps are flying insects, usually black, dark brown or even black with yellow stripes and that, unlike bees, they can sting more than once.
And if there’s one thing these insects are known for, it’s their stinger and their very painful stings, even worse than those of bees. Although its venom is not that powerful, allergic reactions can occur in some people.
Wasps are found in many places around the world. To build their nests, they mainly prefer walls or trees in places where they receive sun and water. Therefore, it is very common to find them in parks and other outdoor areas.
In view of the fact that the nests are usually located in places of habitual transit, it is normal for their space to be ‘invaded’ and for them, in order to defend themselves, to sting. For this reason, wasp stings are much more common in children because, when playing outdoors, they do not know that there are animals ready to defend their territory.

Risks of wasp stings in children
Through their sting, these insects inject a toxic substance that, despite the pain resulting from the bites, does not represent a risk to life. Unless the child is allergic.
Normal reactions, both in children and adults, are usually as follows:
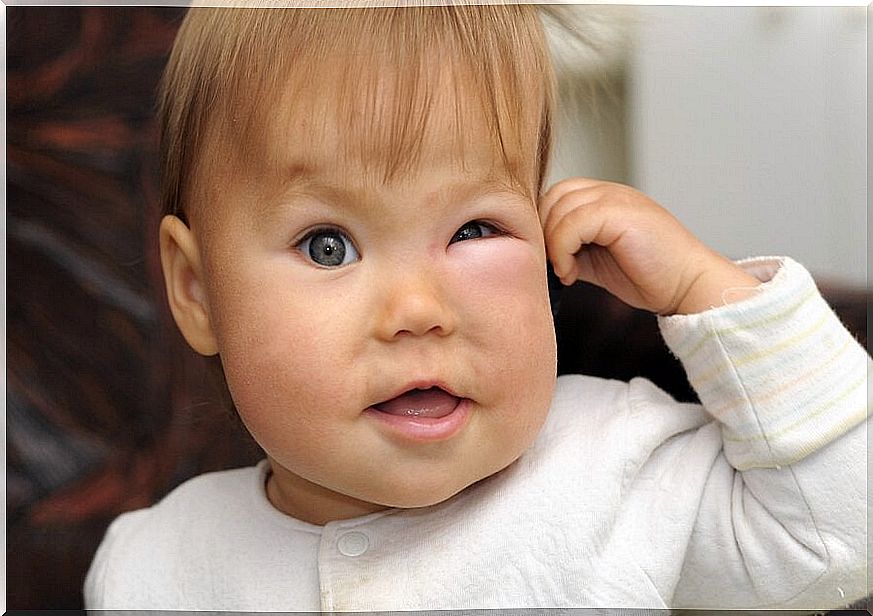
- Redness.
- Swelling of the area.
- Pain of variable intensity, according to the sensitivity of the person or area affected.
Even so, there is an index of danger in wasp stings in children because, although less frequent, they can occur in the throat, face or tongue region and, as a result, the swelling can obstruct the airways.
And what is more evident in children than in adults are allergic reactions. In this case, after the bite, hives may occur in various areas of the body, swelling of the lips, dizziness, vomiting or difficulty breathing.
In the presence of these symptoms, it is necessary to go to the emergency room, as the reaction to wasp stings in children can be very quick. To treat these cases, it is convenient to administer a correct dose of corticosteroid or antihistamine immediately.
Prevention of wasp stings
It is important to teach children to recognize a hornet’s nest. In addition, we must also teach that they should stay away from them and not bother the wasps, because if they feel threatened, they will attack.
On the other hand, children should be informed that if a wasp lands on any part of their body, they should gently push it away. If they try to kill her, they can make her angry and thus create unnecessary conflict. Certainly, sudden movements will cause violent reactions.
What to do after a wasp sting?
Primary Measures
If our children get a wasp sting, the best thing we can do is not to squeeze the area, mainly because it produces more inflammation. It is rare for the stinger to become embedded in the skin as, unlike bees, wasps do not lose it when they attack.
If necessary, disinfected tweezers must be used with care so as not to burst the poison pouch. Then wash the area with water and apply cold compresses to relieve pain and swelling.
Applying some acidic substance to wasp stings in children neutralizes their alkaline poison. Thus, vinegar, lemon juice, baking soda, or ammonia can be used.
These remedies should not be given if the child has severe allergic symptoms, such as a swollen tongue or a feeling of suffocation. In such cases, as mentioned above, we must immediately go to the nearest medical center.
In case of allergy
If there is evidence of being allergic, the child should always carry among their belongings, especially in open areas, the medications indicated by the doctor. Therefore, it should mainly include adrenaline, antihistamines (such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, in a dose according to weight) and corticosteroids.
Also, since adrenaline comes in a pre-filled, self-injecting syringe, both those caring for you and the child, if old enough, should know how to administer it.
The most important thing at all times is to remain calm, both when we encounter these insects and if the child has already been bitten. We must take care of the swelling, try to relieve pain and be aware of any reaction, without altering the child.
Instilling panic at this or any other insect will make the child avoid playing and having fun outdoors, and that is not what we want.
In this sense, we must learn to enjoy and live with nature, and our children must respect and appreciate it. Even though we sometimes have unpleasant encounters with its other inhabitants.