Incubator: What It Is And How It Works
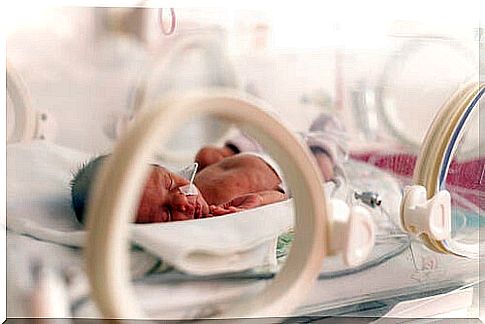
Everyone has seen an incubator at some point in their lives and knows its function well. In this article, we will detail how exactly this wonderful artifact works, which has considerably reduced cases of infant mortality, especially in less developed countries.
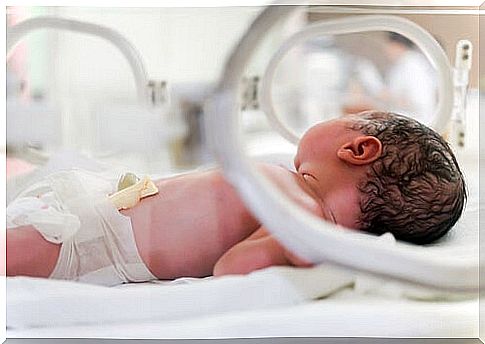
The incubator is a closed chamber that aims to provide an environment conducive to the maturation of premature babies or newborns. It is made of transparent material, has a padding where the baby lies down and has air intakes and windows.
In addition, they include control systems that let you know in real time the child’s weight, heart rate and brain activity. This means that they indicate minute by minute how the baby’s body is functioning.
Incubator Functions
There are certain characteristics that the incubator must have in order to effectively fulfill its objective. These are the main ones:
- Servo control : it is a sensor that is attached to the baby’s skin to measure its temperature. If it is low, the incubator automatically emits heat. If it’s high, it does the opposite.
- Isolation: one of the essential obligations of these devices. The air filters in the incubator keep out germs and allergens inside. This is why it is such an important element for babies with immune system problems.
- Humidity sensors: just as it controls temperature, it measures the humidity inside the incubator. If there is too little moisture, it can lead to the baby’s dehydration.
- Oxygen source: in order to prevent respiratory diseases in newborns, the incubator provides an environment with a lot of oxygen.
- Assisted breathing: in severe cases where babies cannot breathe on their own, they are incubated and a pump is placed to help them complete this process mechanically.
- UV rays: the incubator’s ultraviolet light – which is given in moderate amounts – serves to activate endogenous vitamin D and to combat jaundice, which is the yellowish color perceived in the skin of some newborns.
When do you put the baby in the incubator?
As we stated before, the incubator has fundamental tools for controlling the newborn’s functions. In addition, it allows you to distance yourself from environmental threats that can cause complications in these beings so small and often helpless.
The most common cases in which it is necessary to place the baby in an incubator are these:
- Birth of Premature Babies: A baby is considered premature when he is not more than 37 weeks pregnant. This can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as high blood pressure in the mother or complications in the late stages of pregnancy. The incubator allows the baby to fully develop.
- Low birth weight: A baby is considered to be underweight when he is less than 2.5 kg at birth. Whether it is a normal or premature birth, the incubator is responsible for protecting the baby and administering orally or intravenously the nutrients that your body needs.
- Difficulties in maintaining body temperature: as the incubator has a constant temperature, it allows you to overcome this problem.
- Deficiencies in the immune system: until they develop the capacity to defend themselves against pathogens, babies – usually premature ones – are kept in this environment free of germs and microbes that can pose a threat to health.
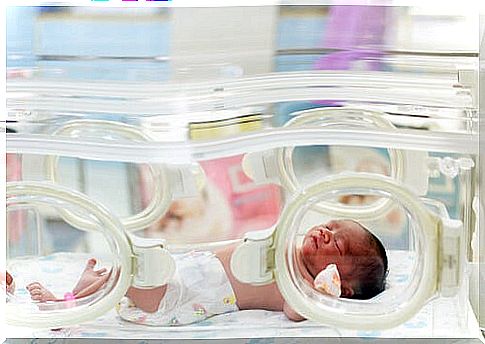
However, it may also be due to other circumstances that the baby needs to stay in an incubator during this period:
- Bone weakness or muscle weakness.
- Lack of lung development.
- Sensorineural development deficit.
- Absence of sucking reflex, which prevents the baby from feeding alone.
What to do if my baby has to stay in an incubator
First, parents should consider that when a baby is in an incubator, it is very well taken care of. Control is constant and your needs are fully met, so don’t worry.
Furthermore, the fact that he needs to stay a few days in the incubator does not mean that his health is at risk. Often, the incubator is used as a period of “adaptation to the world”. Once the baby finishes developing properly, it can return to normal life.
Finally, visiting hours depend on the institution and also on the health situation of each baby. The neonatology session is usually very rigid, so they usually only allow the minimally essential visits.
Try to stay calm and be patient: soon you will be able to enjoy every minute of your day with your child and you will be able to have a completely normal life.